SERVING
Those That
SERVED
PTSD
Post traumatic stress disorder, also known as PTSD, is among only a few mental disorders that are triggered by a disturbing outside event, unlike other psychiatric disorders such as depression.
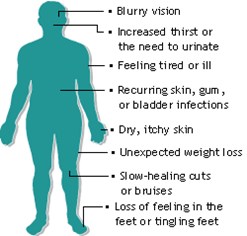
Type II Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, once known as adult-onset or noninsulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic condition that affects the way your body metabolizes sugar (glucose), your body's main source of fuel.
Tinnitus
Tinnitus, is a ringing, swishing, buzzing, or other type of noise that seems to originate in the ear or head. The sound may seem to come from one ear or both, from inside the head, or from a distance.


Presumptive Disabilities
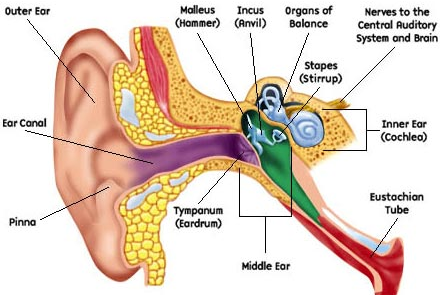
1. Tinnitus
2. Hearing Loss
3. Limitation of Flexion of the Knee
4. Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
5. Lumbosacral or Cervical Strain
6. Scars, General
7. Paralysis of the Sciatic Nerve (Sciatica)
8. Limitation of Range of Motion of the Ankle
9. Migraines (Headaches)
10. Limitation of Motion of the Arm
11. Degenerative Arthritis of the Spine
12. Sleep Apnea
13. Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
14. Major Depressive Disorder
15. Asthma
16. Diabetes Type 2
17. Cancer
18. Generalized Anxiety Disorder
19. Pes Planus (Flat Feet)
20. Radiculopathy
21. Adjustment Disorder
22. Somatic Symptom Disorder (Chronic Pain Syndrome)
23. Gastroesophageal Reflex Disease (GERD)
24. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
25. Erectile Dysfunction
2023 Top 50 Veteran Disabilities
26. Plantar Fasciitis
27. Arthritis
28. Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
29. Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD)
30. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
31. Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS)
32. Fibromyalgia
33. Eczema
34. Allergic Rhinitis (Hay Fever)
35. Sinusitis
36. Meniere’s Syndrome
37. Arteriosclerotic Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease)
38. Chronic Conjunctivitis
39. Limited Motion of the Jaw (Temporomandibular Disorder)
40. Hiatal Hernia
41. Hemorrhoids
42. Varicose Veins
43. Nephrolithiasis (Kidney Stones)
44. Hypothyroidism
45. Anemia
46. Peripheral Neuropathy
47. Prostate Gland Injuries
48. Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)
49. Vertigo
50. Urinary Incontinence
Disease Highlight
Insomnia
Insomnia is a common issue among veterans, often stemming from the psychological and emotional aftermath of their service. Many veterans experience post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), which can manifest through intrusive thoughts, heightened anxiety, and hypervigilance—making it incredibly difficult to relax and fall asleep. Additionally, feelings of depression are prevalent among veterans, further complicating their ability to achieve restorative sleep. The transition from military to civilian life can also introduce new stresses that disrupt established sleep patterns, leading to feelings of isolation, despair, and their inability to hold down gainful employment.
How VA Rates Insomnia
VA rates insomnia as a mental health disorder, such as PTSD or depression. The rating percentages assigned to mental health disorders are:
-0%: A mental condition has been formally diagnosed, but symptoms are not severe enough either to interfere with occupational and social functioning or to require continuous medication.
-10%: Occupational and social impairment due to mild or transient symptoms which decrease work efficiency and ability to perform occupational tasks only during periods of significant stress, or symptoms controlled by continuous medication.
-30%: Occupational and social impairment with occasional decrease in work efficiency and intermittent periods of inability to perform occupational tasks (although generally functioning satisfactorily, with routine behavior, self-care, and conversation normal), due to such symptoms as: depressed mood, anxiety, suspiciousness, panic attacks (weekly or less often), chronic sleep impairment, mild memory loss.
-50%: Occupational and social impairment with reduced reliability and productivity due to such symptoms as: flattened affect; circumstantial, circumlocutory, or stereotyped speech; panic attacks more than once a week; difficulty in understanding complex commands; impairment of short- and long-term memory; impaired judgment; impaired abstract thinking; disturbances of motivation and mood; difficulty in establishing and maintaining effective work and social relationships.
-70%: Occupational and social impairment, with deficiencies in most areas, such as work, school, family relations, judgment, thinking, or mood, due to such symptoms as: suicidal ideation; obsessional rituals which interfere with routine activities; speech intermittently illogical, obscure, or irrelevant; near-continuous panic or depression affecting the ability to function independently, appropriately and effectively; impaired impulse control; spatial disorientation; neglect of personal appearance and hygiene; difficulty in adapting to stressful circumstances; inability to establish and maintain effective relationships.
-100%: Total occupational and social impairment.
A diagnosis of insomnia, without other concomitant mental disorders, typically receives, at least initially, a 30% rating for chronic sleep impairment. (Hill & Ponton)